|
Tamron AF 24-70mm f/2.8 SP Di USD VC (Canon EOS) - Full Format Review / Lens Test - Analysis |
|
Lens Reviews -
Canon EOS (Full Format)
|
|
Page 2 of 3

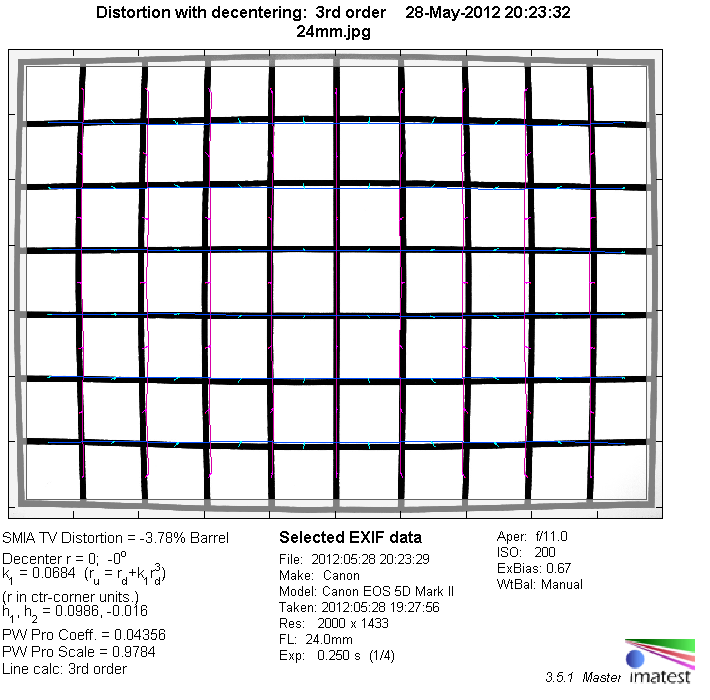
Distortion
At 24 mm the lens shows a heavy amount of barrel distortion (~3.8%), which flips over to a slight pincushion type (~0.8%) at 70mm. In the middle range distortion is marginal.
|
Move the mouse cursor over the focal length text marks below to observe the respective distortion
|
| 24mm |
35mm |
50mm |
70mm |
|
|
The chart above has a real-world size of about 120x80cm.
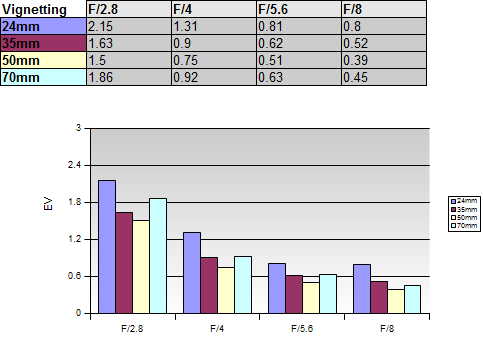
Vignetting
At 24mm f/2.8 the amount of vignetting is very pronounced at more that 2EV (f-stops) but can be decreased by stopping down. However, even stopped down to f/8 light falloff remains a bit on the high side and can still be seen in critical scenes. Things look similar albeit slight better at other focal lengths - very visible vignetting wide open but stopping down helps to decrease the amount considerably. Regarding its ultra-large front element we hoped that the lens performed a little better here.
MTF (resolution)
The lens delivered very solid resolution figures in the MTF lab. At 24mm the center resolution is already superb at f/2.8. The border/corner quality is on a good level at large apertures and improves to very good border results from f/4 onward. The corners require f/8 to jump across this rating barrier. This pattern is also roughly valid for the 35mm and 50mm settings. At 70mm we are seeing a slight decrease in center performance at f/2.8. The contrast level is also slightly reduced here. However, the center is excellent from f/4 onward and the lens delivers very high quality results across the frame from f/5.6 to f/11. At f/11 there's a slight hint of diffraction (reduces the image quality) so you should avoid to choose an aperture beyond this setting if possible.
The Tamron lens has only a slight amount of field curvature throughout the zoom range which is certainly an advantage of the Canon EF 24-70mm f/2.8 USM L (I).
The centering quality of the tested sample was generally good from a lab perspective. We have experienced one outlier during the field session - see the church sample in the image sample section. This may have related to a VC effect.
Please note that the MTF results are not directly comparable across the different systems!
Below is a simplified summary of the formal findings. The chart shows line widths per picture height (LW/PH) which can be taken as a measure for sharpness.
If you want to know more about the MTF50 figures you may check out the corresponding Imatest Explanations
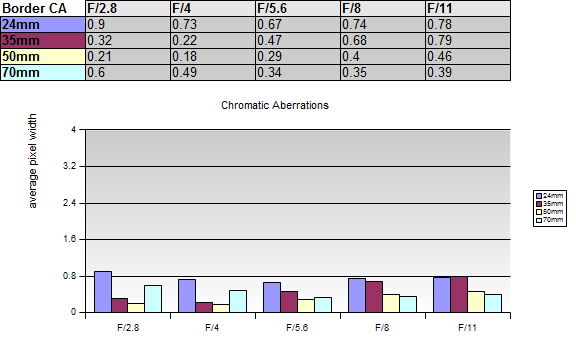
Chromatic Aberrations (CAs)
Chromatic aberrations (color shadows at harsh contrast transitions) are very well controlled and not relevant at all tested aperture settings and focal lengths. This is quite impressive.
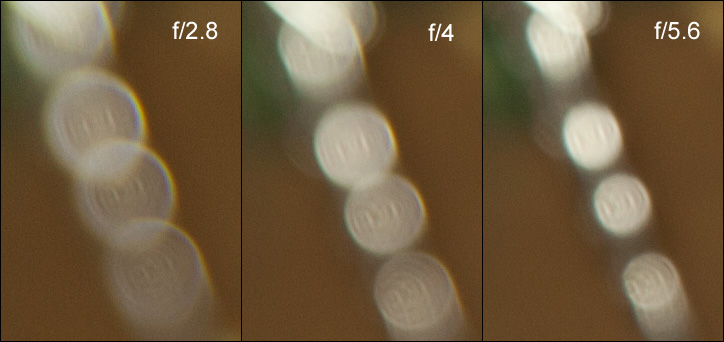
Bokeh
Being a fast lens, it allows for good subject separation and thus the quality of out-of-focus blur is certainly of interest. We looked at bokeh with our standard test scene at 70mm focal length, which is closest to classic head to shoulder portrait lenses (~85mm).
The general quality of the background blur is quite smooth (see the left sample crop below). However, the foreground blur is more busy (to the right).
 Thanks to 9 rounded aperture blades, background highlights retain their circular shape throughout the whole aperture range. However, the inner area of the highlight disc is rather nervous - possibly a side effect of the aspherical elements. The highlight discs deteriorate a bit towards the usual "cat's eye" towards the borders. This effect can be reduced by stopping down. The highlight discs (in the center) remain circular even at f/5.6 so the design of the rounded aperture blades is obvious here.
Thanks to 9 rounded aperture blades, background highlights retain their circular shape throughout the whole aperture range. However, the inner area of the highlight disc is rather nervous - possibly a side effect of the aspherical elements. The highlight discs deteriorate a bit towards the usual "cat's eye" towards the borders. This effect can be reduced by stopping down. The highlight discs (in the center) remain circular even at f/5.6 so the design of the rounded aperture blades is obvious here.
Bokeh Fringing / Longitudinal Chromatic Aberrations (LoCA)
LoCAs (non-coinciding focal planes of the various colors) are a common issue with relatively fast glass - they are often noticeable in out-of-focus halos: magenta (red + blue) in front the focus point and green beyond. Surprisingly the Tamron is only marginally affected.
If you scroll through the images below you may notice a slight shift in focus when stopping down. This is a so-called "residual spherical aberration".
|
Move the mouse cursor over the f-stop marks below to observe the respective LoCAs
|
| f/2.8 |
f/4.0 |
f/5.6 |
|

|
|